Smart Agro IoT
Internet of Things New digital agriculture is made possible by smart technology. By optimizing the use of fertilizer to increase plant efficiency, advanced agriculture, which is based on Internet of Things technology, is intended to enable producers and farmers to reduce waste and improve production. It allows farmers more control over their animals, crop growth, cost and resource reduction, and livestock.

Use Cases
Monitoring of climate conditions
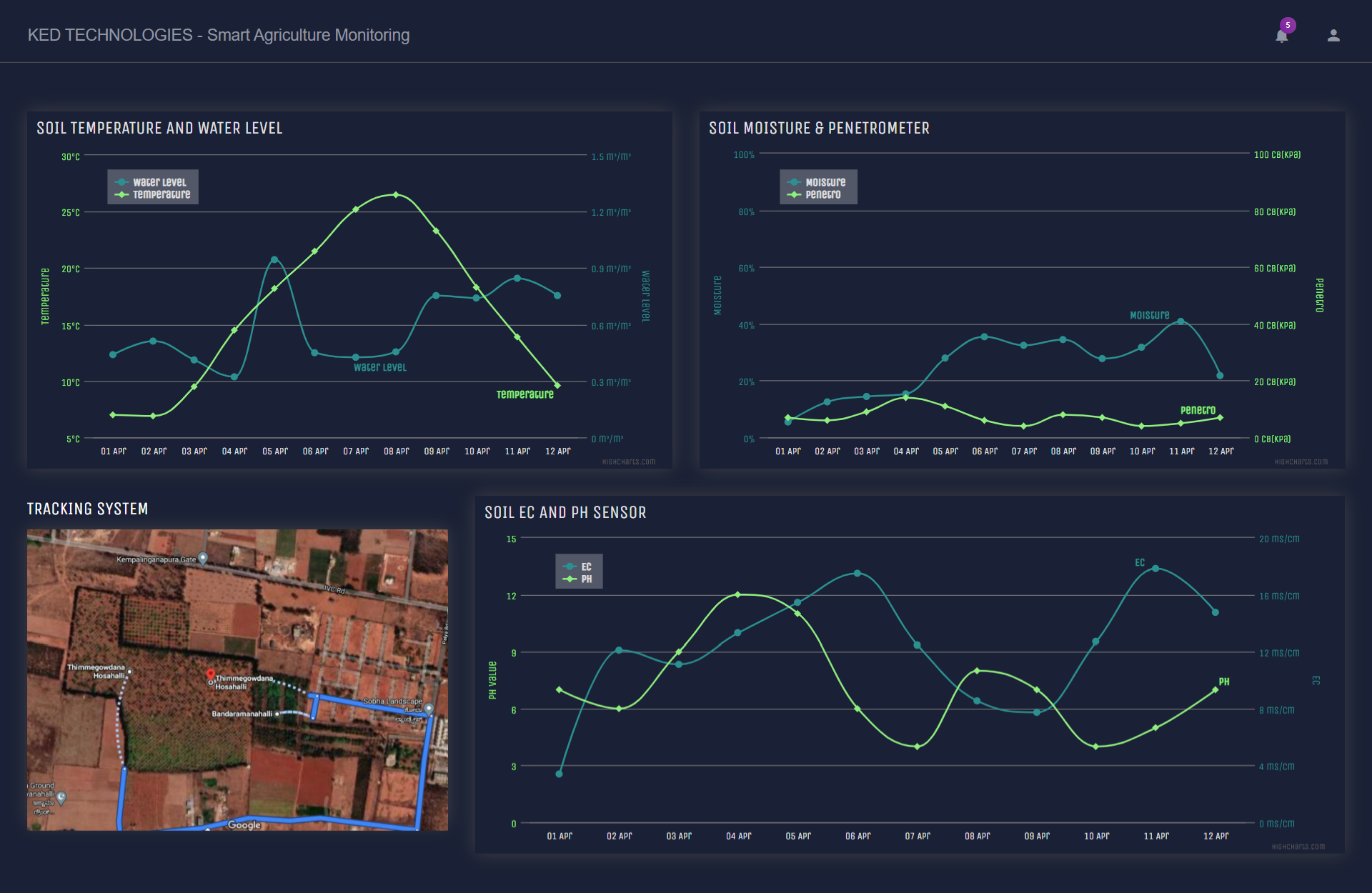
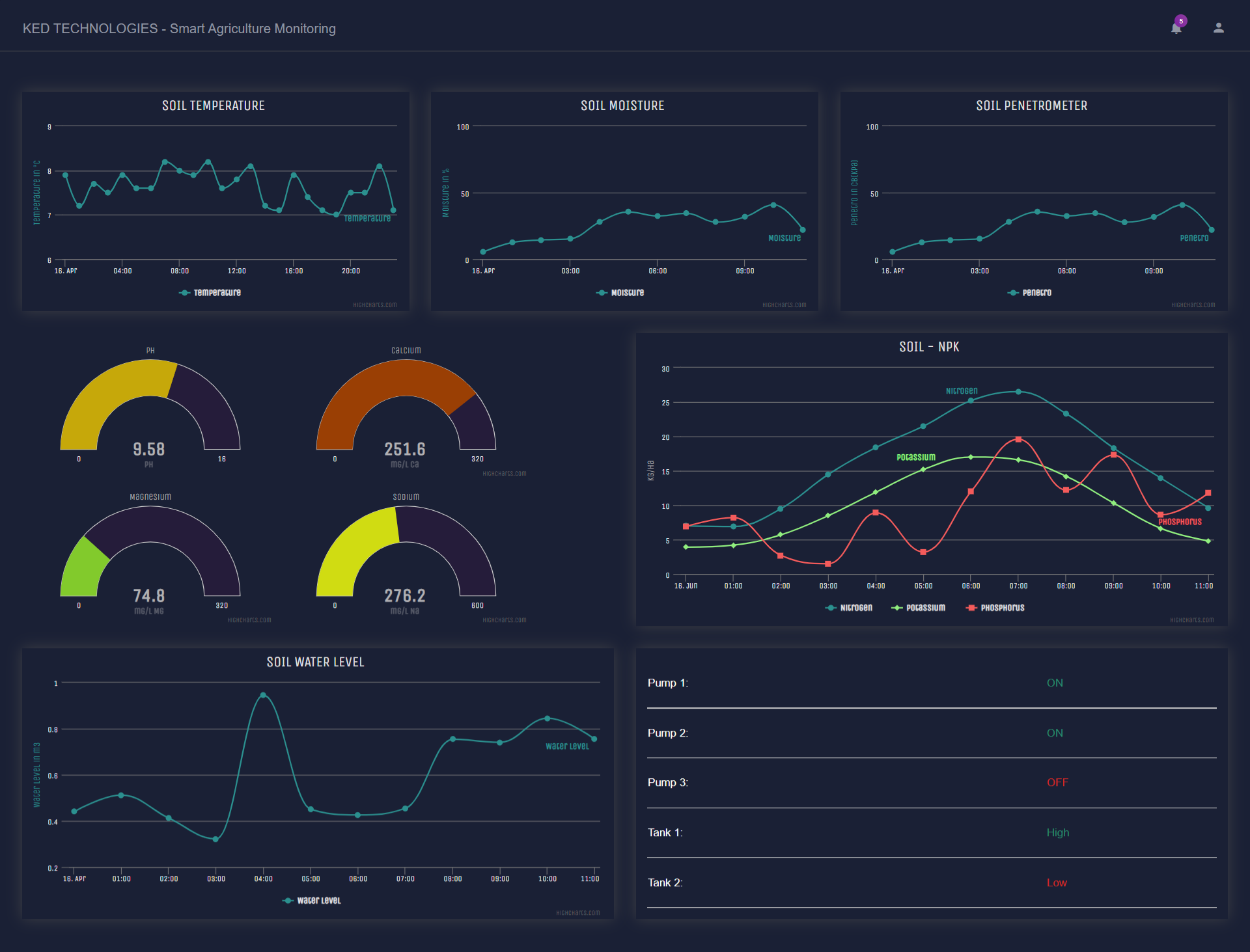
Probably the most popular smart agriculture gadgets are weather stations, combining various smart farming sensors. Located across the field, they collect various data from the environment and send it to the cloud. The provided measurements can be used to map the climate conditions, choose the appropriate crops, and take the required measures to improve their capacity (i.e., precision farming).
Crop management
One more type of IoT product in agriculture and another element of precision farming are crop management devices. Just like weather stations, they should be placed in the field to collect data specific to crop farming; from temperature and precipitation to leaf water potential and overall crop health.
Cattle monitoring and management
Just like crop monitoring, there are IoT agriculture sensors that can be attached to the animals on a farm to monitor their health and log performance. Livestock tracking and monitoring help collect data on stock health, well-being, and physical location.
Water Management
The Soil sensors give us the accurate data which allow us to control and monitor the water required for the field which could help in using it effectively without wastage and making it work remotely without any human interference.
Precision farming
Also known as precision agriculture, precision farming is all about efficiency and making accurate data-driven decisions. It is also one of the most widespread and effective applications of IoT in agriculture.
By using IoT sensors, farmers can collect a vast array of metrics on every facet of the field microclimate and ecosystem: lighting, temperature, soil condition, humidity, CO2 levels, chlorophyll content, Refractive index, and pest infections. This data enables farmers to estimate optimal amounts of water, fertilizers, and pesticides that their crops need, reduce expenses, and raise better and healthier crops.
Agricultural drones
Perhaps one of the most promising advancements is the use of agricultural drones in smart farming. Also known as UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles), drones are better equipped than airplanes and satellites to collect agricultural data. Apart from surveillance capabilities, drones can also perform a vast number of tasks that previously required human labour: planting crops, fighting pests and infections, agriculture spraying, crop monitoring, etc.
GPS Tracking
Perhaps the GPS positioning of the farm vehicle i.e., the tractors would help in monitoring the exact location of the ploughed field and give us a data of the left-out field, while the tractors are nowadays smart enough to operate on their own.
Bird Scarer
Using Remote Outdoor speaks which is controlled through IoT Devices and Night Flashlight for scaring animals in the agriculture field.